Treated conditions
Home » Areas of expertise » Dural Arterio-Venous Fistulas
Treated conditions
Dural Arterio-Venous Fistulas
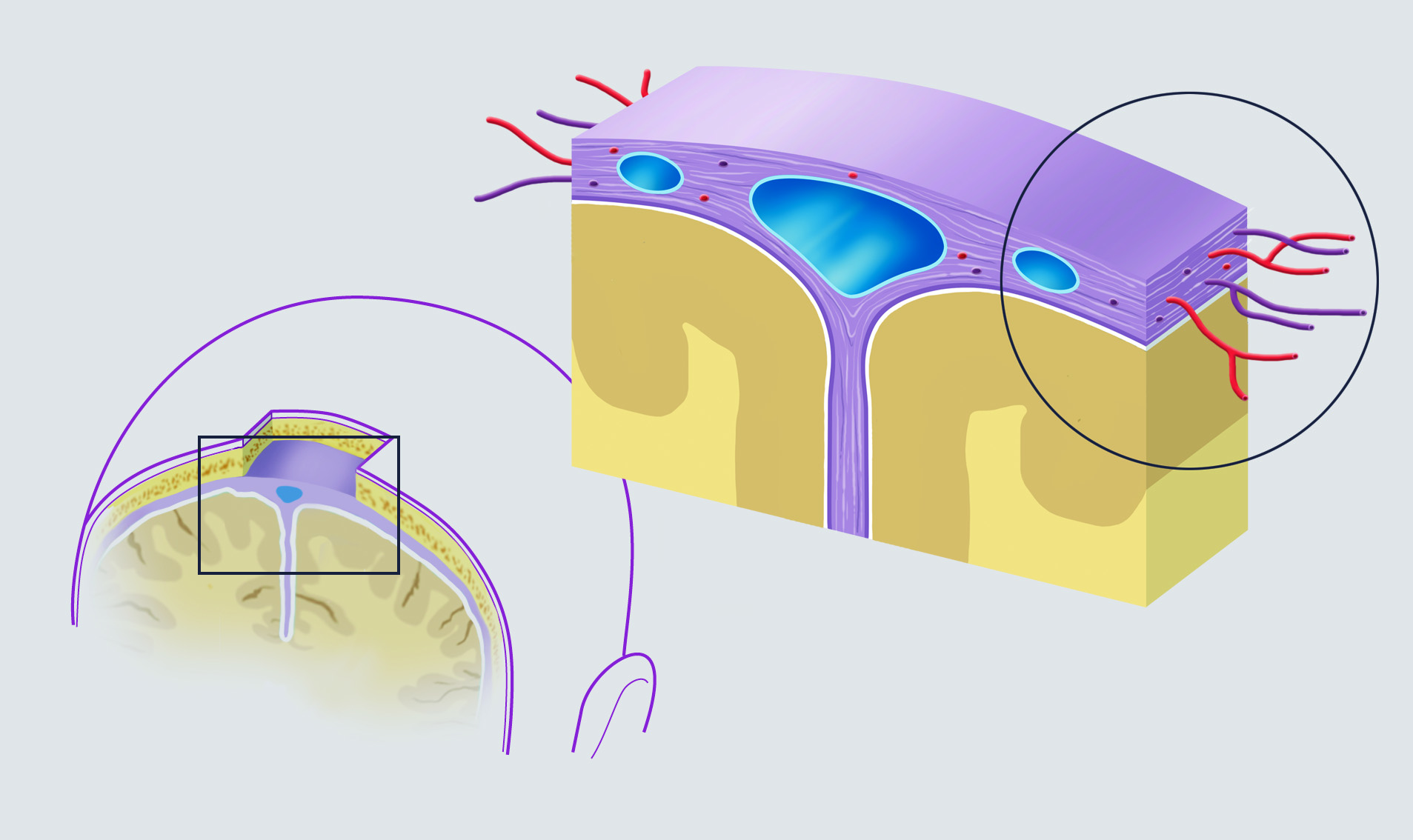
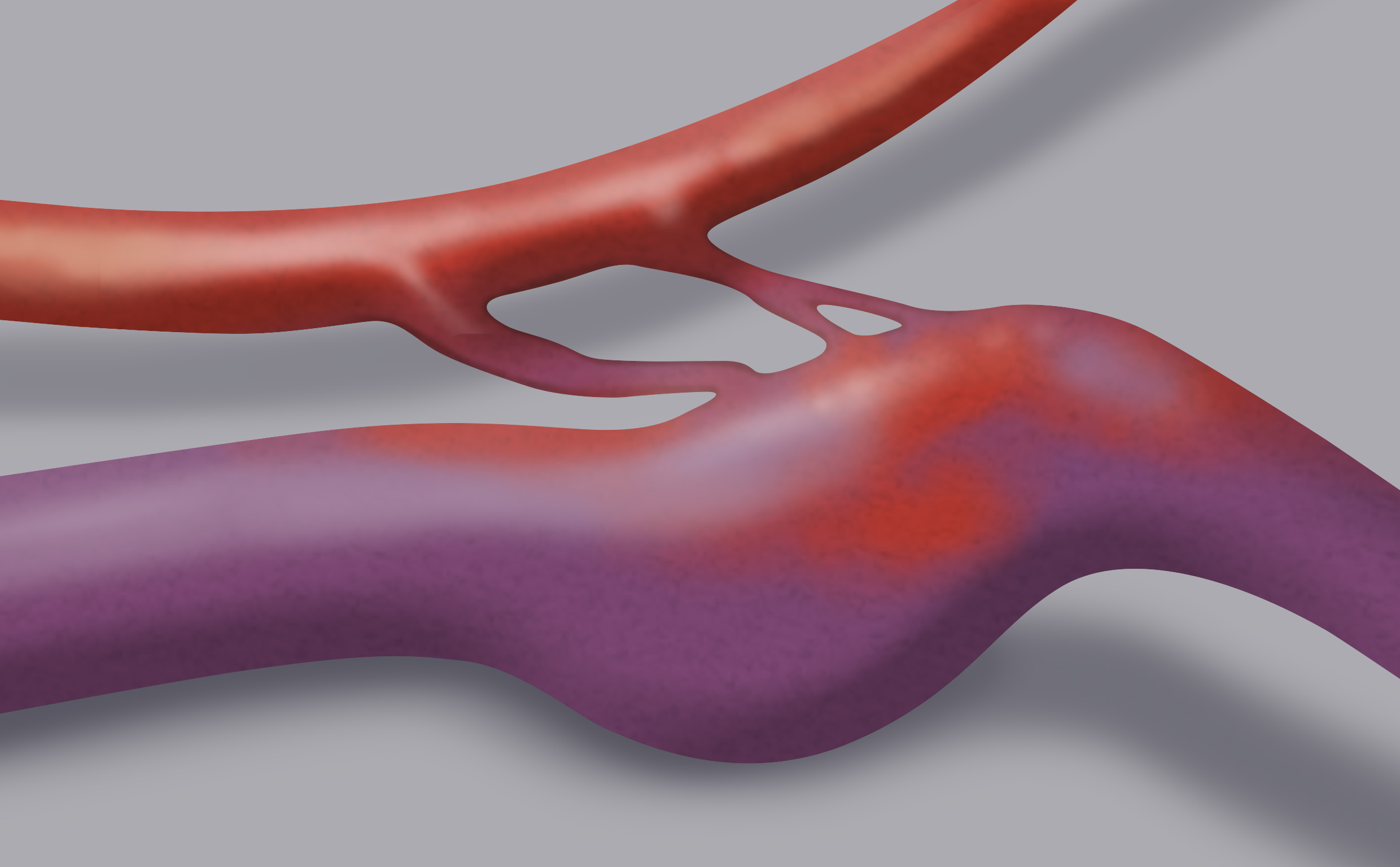
The dural arterio-venous fistula (dAVF) is a vascular malformation constituted by an anomalous communication between an artery and a vein. The passage between them is direct, without the interposition of a capillary bed, located in the territory of the dura mater (one of the three layers that make up the meninges).
The afferent artery is generally a meningeal artery that flows into an arterial reticulum (nidus) located within the thickness of the dura mater. From here, some discharge veins depart (arterialised veins because they transport blood with arterial pressure), which often converge into a dural venous sinus. The direct arterio-venous communication determines a pressure overload in the venous structures composing the fistula. In the event that it involves other cerebral veins, this overload may cause brain hemorrhage.
The pathogenic mechanism is unknown, but a correlation between cardiovascular diseases, previous craniotomies, thrombosis of the dural venous sinuses and the development of dAVF has been observed.
The hypothesis of a possible infectious origin is also particularly accredited.
Dural arterio-venous fistulas can be both cerebral and spinal, i.e. located in a territory of the dura mater that surrounds the spinal cord.
Symptoms
Dural intracranial arterio-venous fistulas can cause hemorrhage or cerebral hemorrhagic infarcts with serious neurological consequences.
In spinal dAVFs, on the other hand, the symptoms are often characterised by increasingly serious disturbances to the lower or upper limbs depending on the location.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis can be reached with angiography: under local anaesthesia, a catheterisation of the femoral artery is performed at the groin so the cerebral or spinal vessels can be reached to inject the contrast medium and highlight the premature visualisation of a vein in the arterial phase.
Treatment
Generally, all dural fistulas with venous hypertension and flow inversion in the other veins should be treated in order to eliminate the risk of hemorrhage and neurological deficits.
Treatment can be surgical or endovascular.
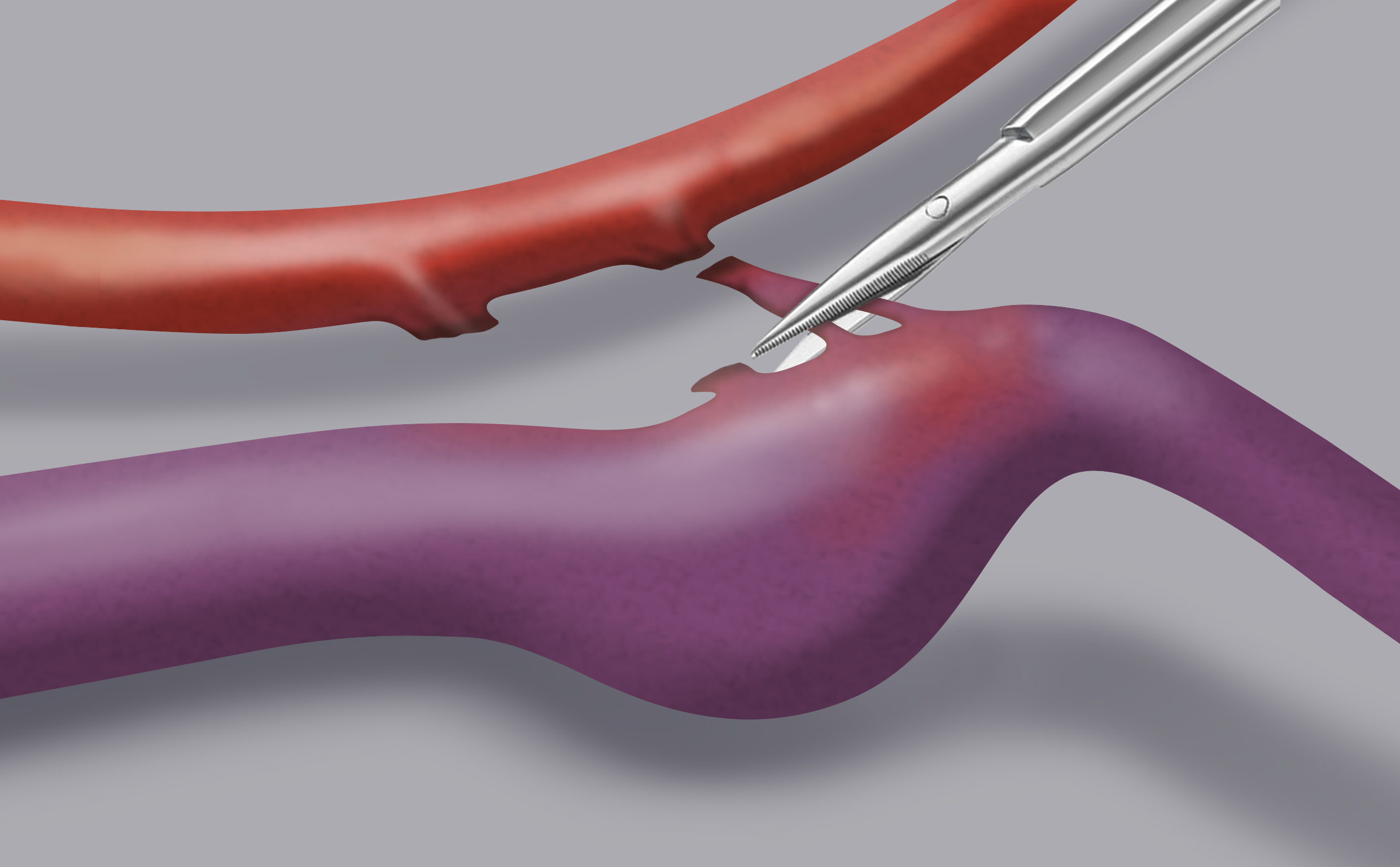
Microsurgical treatment consists in the direct surgical closure of the anomalous arterio-venous passage, as close as possible to the latter’s exit from the dura mater.
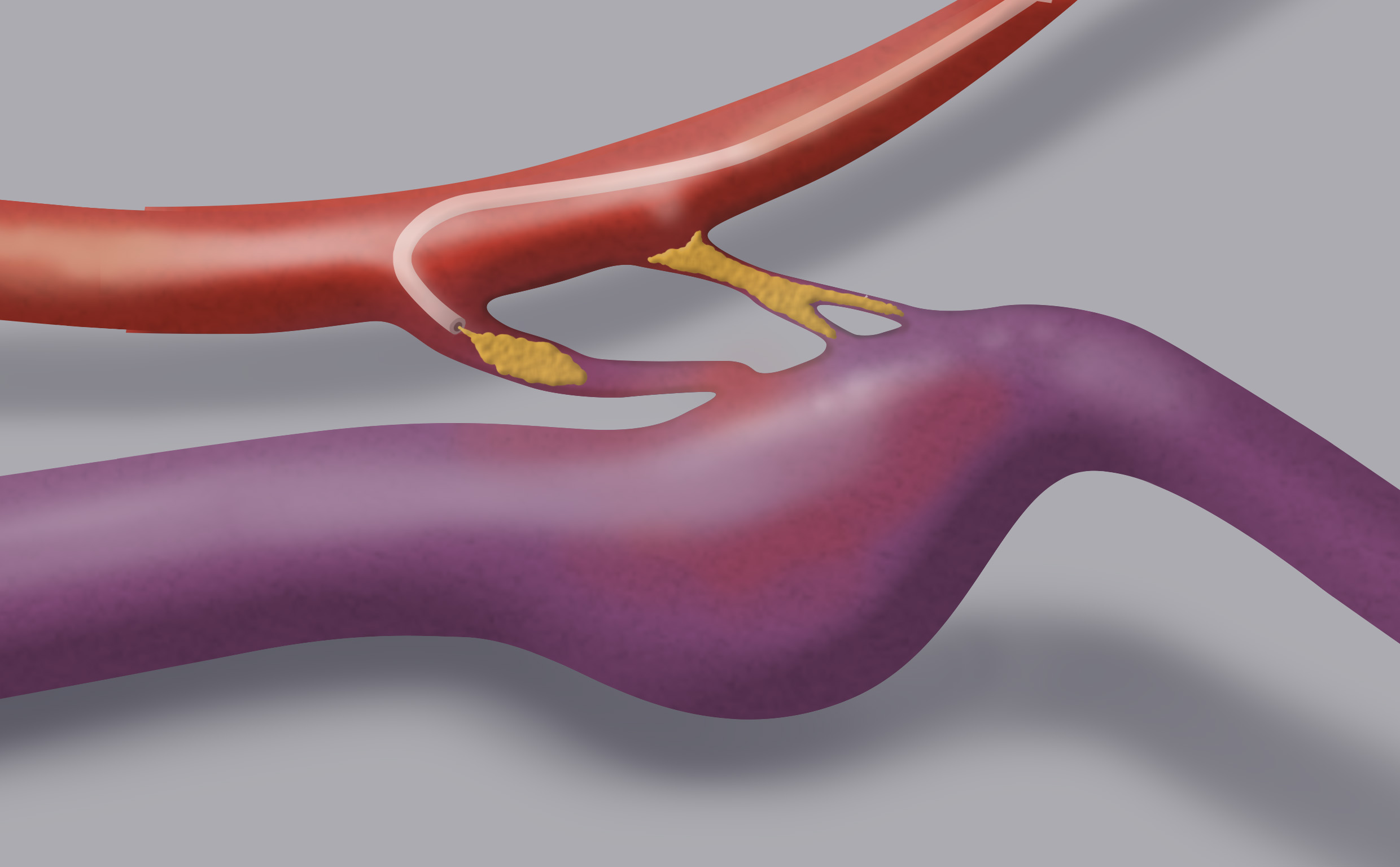
Endovascular treatment can be arterial or venous, depending on if you go through the arterial or venous flow, but both have the aim of reaching the point of the fistula with a microcatheter and occlude it by injecting a glue.