Treated conditions
Home » Areas of expertise » Cerebral Meningiomas
Treated conditions
Cerebral Meningiomas
Cerebral meningiomas are predominantly benign tumors originating from the meninges, the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. They represent approximately 25% of all brain tumors. They typically affect adults aged 40 to 65 years and are more common in women than in men, with a 2:1 ratio. In 25% of cases, they are associated with neurofibromatosis type 2, a genetic syndrome.
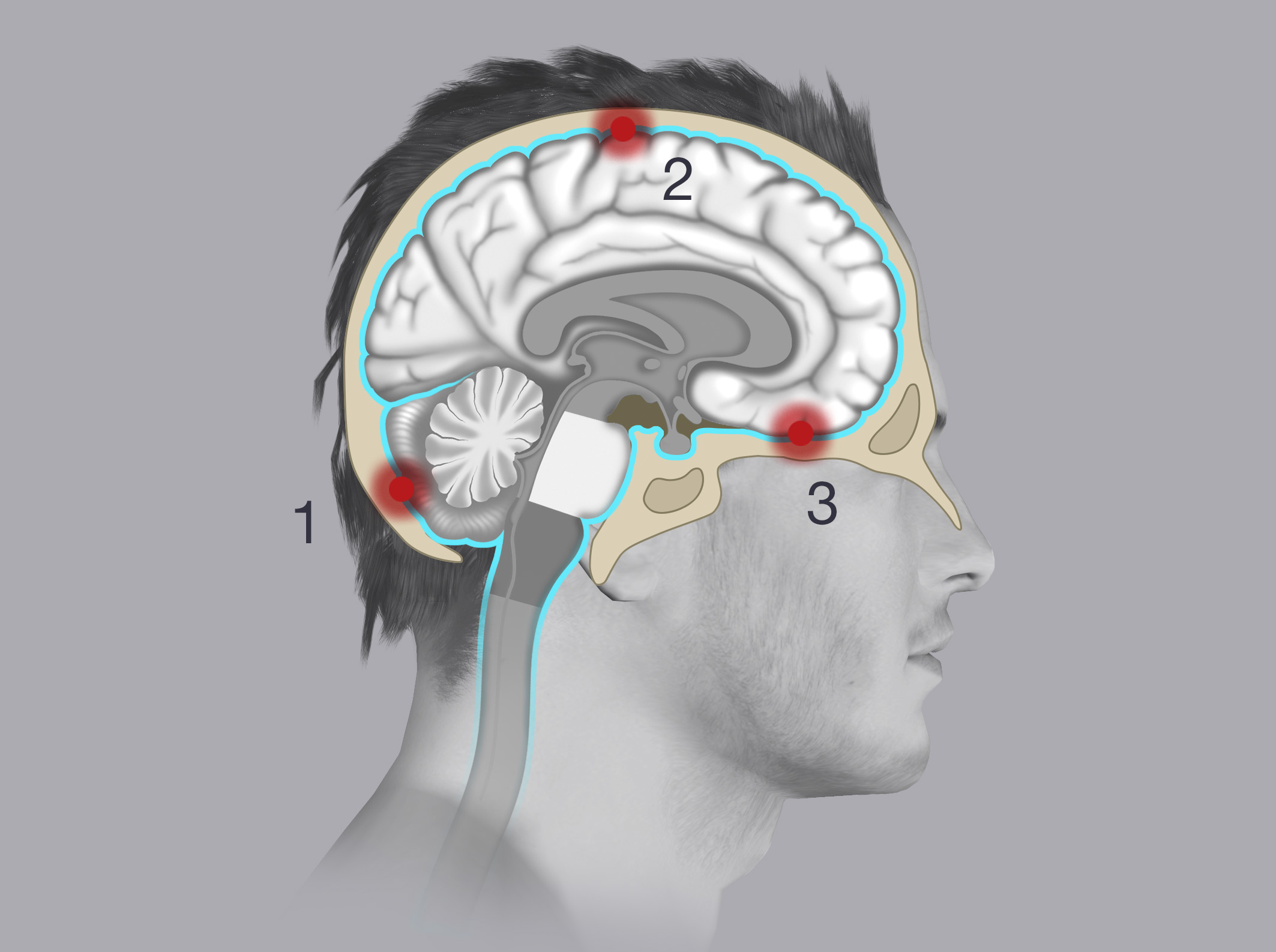
Based on location, meningiomas are classified into:
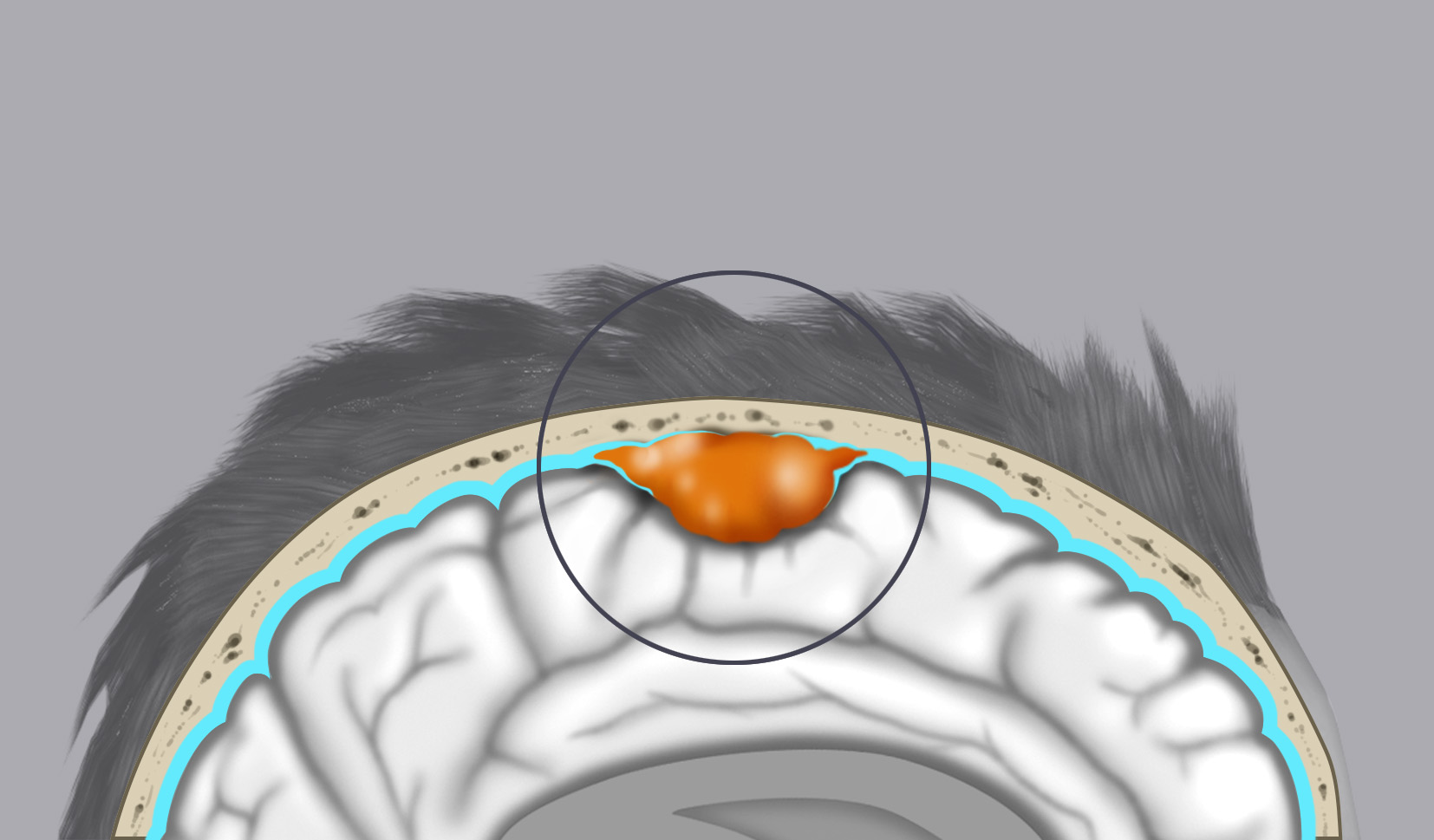
- Convexity meningiomas
- Skull base meningiomas
- Posterior fossa meningiomas
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies meningiomas based on biological aggressiveness into:
- Benign meningiomas (Grade I): About 80% of cases. These are benign, slow-growing tumors that do not infiltrate brain parenchyma and have a low tendency to recur.
- Atypical meningiomas (Grade II): About 10-15% of cases. These tumors have intermediate biological aggressiveness and tend to recur over time.
- Anaplastic meningioma (Grade III): The rarest, with an incidence of 2-3% of cases. These are considered malignant due to their high biological aggressiveness. Unlike benign meningiomas, they can infiltrate brain parenchyma and bone structures and frequently recur.
The etiology of these tumors is unknown. There is some correlation between hormonal regulation alterations and the genesis of meningiomas in women. In females, there is a correlation between the development of breast tumors and meningiomas.
Symptoms
Most meningiomas are asymptomatic due to their small size and are often diagnosed incidentally during investigations for other reasons. Symptoms result from direct compression of adjacent nervous structures by the meningioma and the often associated edema. Symptoms vary depending on the meningioma’s location.
Convexity meningiomas commonly cause:
- Headache
- Seizures
- Mental confusion
- Behavioural alterations
- Language disturbances
- Reduced strength on the side of the body opposite the meningioma
Skull base meningiomas commonly cause:
- Visual disturbances
- Reduced sense of smell
- Eye movement disturbances
Posterior fossa meningiomas commonly cause:
- Balance disturbances
- Motor coordination changes
- Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure (headache, vomiting, drowsiness, stupor) due to compression of structures involved in cerebrospinal fluid outflow, leading to accumulation (hydrocephalus).
Diagnosis
Radiological diagnosis of meningioma is achieved through CT and MRI with contrast, allowing recognition of the lesion’s morphological characteristics, which appear rounded and with regular margins. MRI further defines the tumor’s relationships with adjacent nervous structures.
Treatment
The primary treatment for meningiomas is microsurgical removal, which can often be total and lead to complete recovery. In cases where complete removal is not possible due to proximity to delicate neurovascular structures, patients can undergo subsequent radiosurgery to halt tumor growth. In anaplastic meningiomas, post-surgical radiation therapy is recommended.