Treated conditions
Home » Areas of expertise » Cerebral Aneurysm
Treated conditions
Cerebral Aneurysm
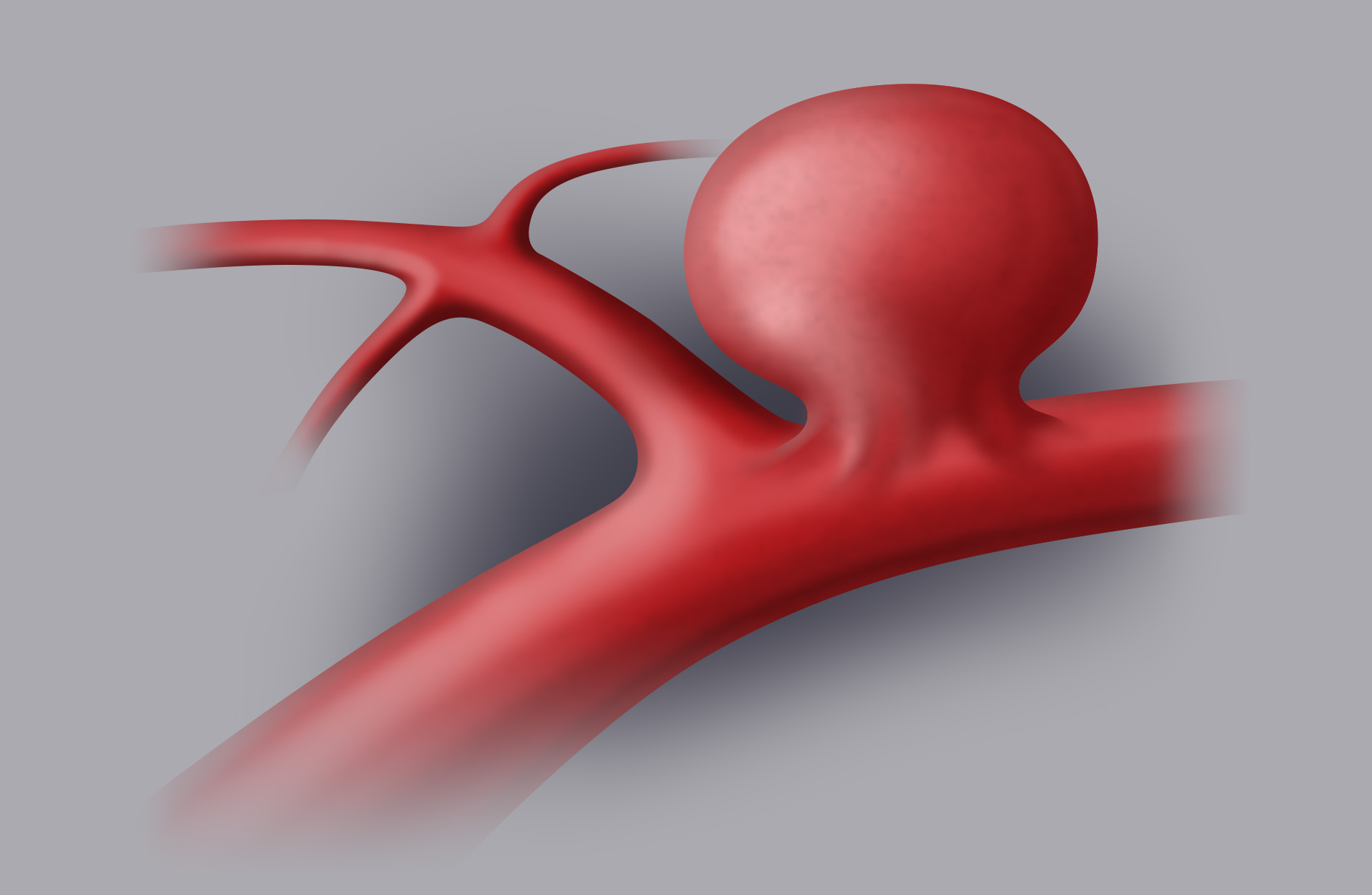
A cerebral aneurysm is a localised dilation of a cerebral artery.
It is a congenital malformation (only in rare cases it can be caused by traumatic brain injury or by a fungal infection) located in the cerebral arteries of the Willis cerebral arterial circle, in particular wherever arteries bifurcate, a point that is subjected to a higher level of stress from the pressure of the blood flow. The arterial wall bulges and forms a “balloon”, defined as an aneurismatic bag, where a neck (the base of the malformation that connects it to the artery it originates from) and a dome can be made out. Aneurysms can be single (70-75%) or multiple (25-30%). Their main location (>90%) is the internal carotid artery and the anterior circle, and more precisely:
- Anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and Anterior Communicating Artery (ACoA): 40%
- Middle cerebral artery (MCA): 35%
- Posterior communicating artery (PCoA): 20%
- Posterior circle: 5%
They are more frequent in women with a 3:1 ratio over men.
When a cerebral aneurysm is close to rupture, it causes an intracranial hemorrhage, which can vary from a small subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) to the formation of voluminous intracerebral hematomas.
About 6% of the population carries a cerebral aneurysm but, fortunately, the cases of rupture are much lower, equal to 10-15 cases/100,000 inhabitants per year.
Depending on their size, cerebral aneurysms can be classified into:
- Small: i.e. with a diameter of less than 7 mm
- Medium: diameter between 7 and 12 mm
- Large: diameter from 13 to 24 mm
- Giant: diameter of more than 25 mm
Symptoms
Most aneurysms remain silent throughout the patient’s entire life. Some symptoms related to the mass effect of the aneurysm dome on the surrounding neural structures may arise (e.g. reduction of visual acuity or paralysis of the 3rd or 6th cranial nerve with consequent disturbances of the eye movements).
In cases in which the aneurysm is close to rupture, the clinical condition changes drastically.
In this case, the symptoms are:
- sudden and violent headache, often located in the lower back of the head, defined as a “stabbing pain” or “the worst headache of my life”
- vomiting
- nuchal rigidity
- photophobia
- seizures
- fever
- reduction of the state of consciousness including coma
In 30% of all cases, a confirmed hemorrhage is preceded by slight episodes of headache (“sentinel” headaches) caused by small bleedings or by an increase in the aneurysm’s volume prior to its rupture.
Diagnosis
More and more often, unruptured cerebral aneurysms are diagnosed coincidentally by means of brain MRI performed for other reasons. In case of a diagnostic suspicion, the brain MRI can be completed with sequences of Angio-MRI.
In the event of symptoms deriving from a suspected aneurysm rupture, patients reach the emergency room where they are subjected to brain CT to detect the possible cerebral hemorrhage. If the latter presents characteristics of a subarachnoid hemorrhage, a brain Angio-CT must be performed promptly (a contrast-enhnced CT in which the morphology of the cerebral arteries, and therefore of the possible aneurysm, is reconstructed). This makes it possible to obtain diagnostic images within a very short time and without invasive procedures.
Should the Angio-CT images be negative or lead to a doubtful interpretation, a cerebral angiography must be performed, which for many years has been considered the medical examination of reference for aneurysm diagnosis. However, recently the introduction of the Angio-CT and the Angio-MRI has significantly reduced its use for diagnostic purposes, although it is fundamental for interventional procedures.
Treatment
As far as the treatment of cerebral aneurysms is concerned, we should distinguish between the diagnosis of incidental aneurysm (unruptured) and a cerebral hemorrhage caused by a bleeding aneurysm.
Incidental aneurysms
More and more frequently, people casually discover having a cerebral aneurysm. The question that the patient asks in this case is always the same: what should I do?
Once the cerebral aneurysm has been diagnosed, the following factors should be determined:
- the size and morphology of the aneurysm
- the location of the aneurysm
- the age and general health conditions of the patient
- any risk factors for sac rupture (smoking, hypertension, familiarity…)
- presence of multiple cerebral aneurysms
- patient’s acceptance of the idea of having an aneurysm and not treating it, an aspect that should not be underestimated.
The size of the sac is directly correlated with the risk of rupture. Multi-centre international studies. such as the ISUIA (International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms) and the UCAS (Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysms Study) have quantified a concrete risk of rupture for aneurysms with a 7 mm diameter or higher, while the risk of a hemorrhage is low (but not equal to zero!) if the diameter is lower than 7 mm.
This means there is a “grey zone” around 4-7 mm in which it is necessary to carefully assess the situation to correctly quantify the risk/benefit ratio of the treatment with respect to the choice of not intervening.
Ruptured aneurysms
In case of a diagnosis of cerebral hemorrhage caused by aneurysm rupture, on the other hand, intervention is, in most cases, a necessary choice (provided, of course, that the clinical and neurological conditions of the patient allow it).
It should be stressed that 50% of all patients affected by cerebral hemorrhage caused by the rupture of an aneurysm face death within 30 days of the event even if they are subjected to the most suitable treatment.
This is because, apart from the direct damage to the brain structures caused by the blood leakage, cerebral hemorrhage can lead to severe complications such as intracranial hypertension and vasospasm, an event that consists in the reduction of the artery caliber until their complete occlusion, consequently provoking compromising cerebral ischemias.
This means that prompt treatment is imperative, since the risk of an aneurysm’s rebleeding is very high in the first days after rupture. As can be easily deduced, the occurrence of a second hemorrhage at a short distance from the first leads to serious consequences: rebleeding implies an increase in mortality equal to about 75%.
Cerebral aneurysms can be treated in two ways:
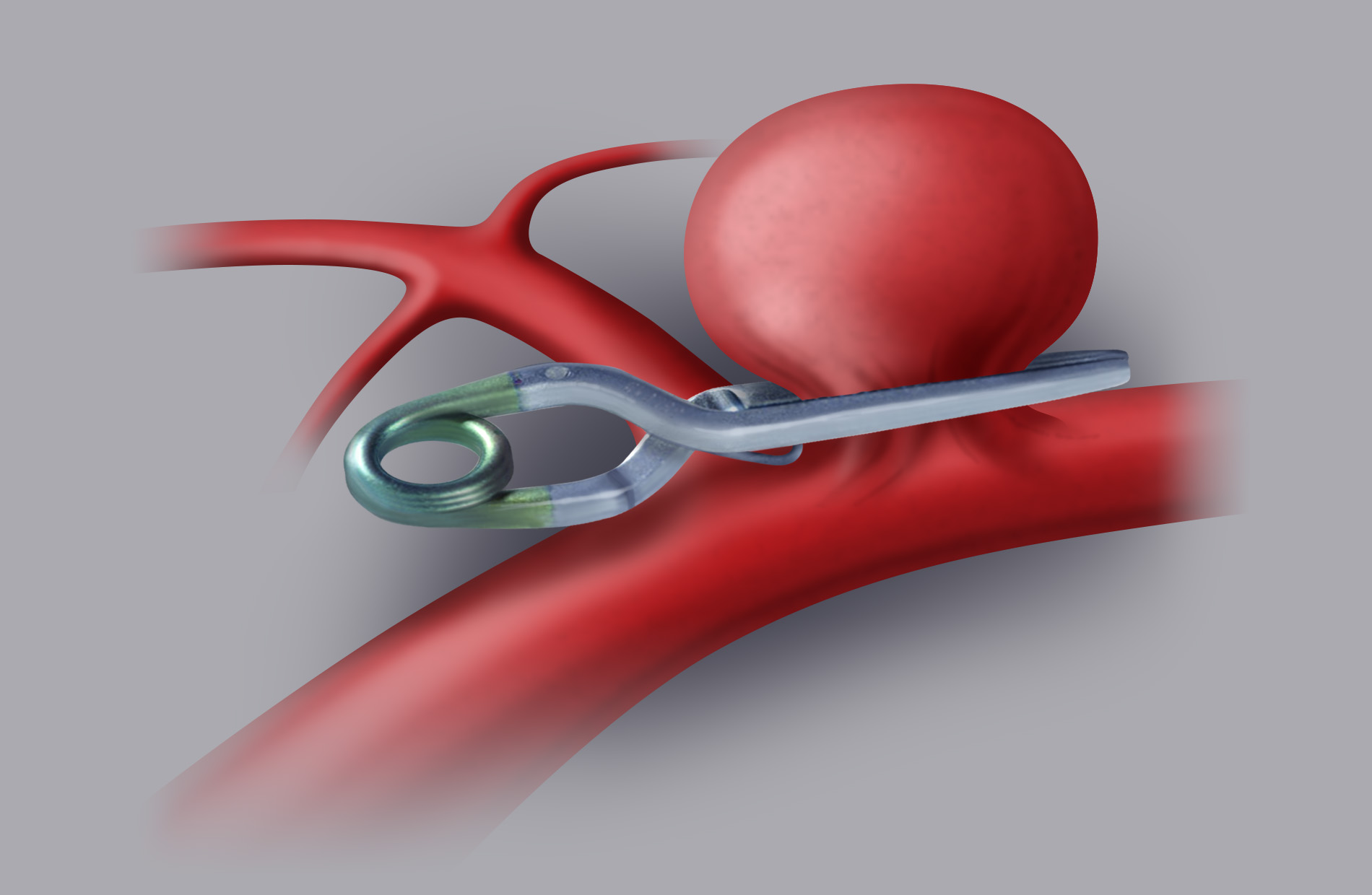
Surgical treatment (clipping)
The craniotomy approach makes it possible to visualise the cerebral arteries and identify the aneurysm, which can then be excluded from cerebral circulation by applying one or more clips (small titanium clips) on the neck of the aneurysm.
This procedure is performed with the support of the most advanced technology:
- Operating microscope with intraoperative fluorangiography
- Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring
- 3D endoscopy
- Flowmetry and intraoperative microdoppler
All these devices help the neurosurgeon to make sure that the aneurysm is excluded and that the surrounding arteries remain patent.
The risks are mainly associated with the location, morphology and size of the aneurysm, apart from on the neurosurgeon’s degree of experience. The surgeon should have performed various procedures in this field to guarantee excellent safety standards.
In non-ruptured cerebral aneurysm surgery the risks are contained, and normally patients are released after 4-5 days of hospitalization, with a convalescence of about 30 days.
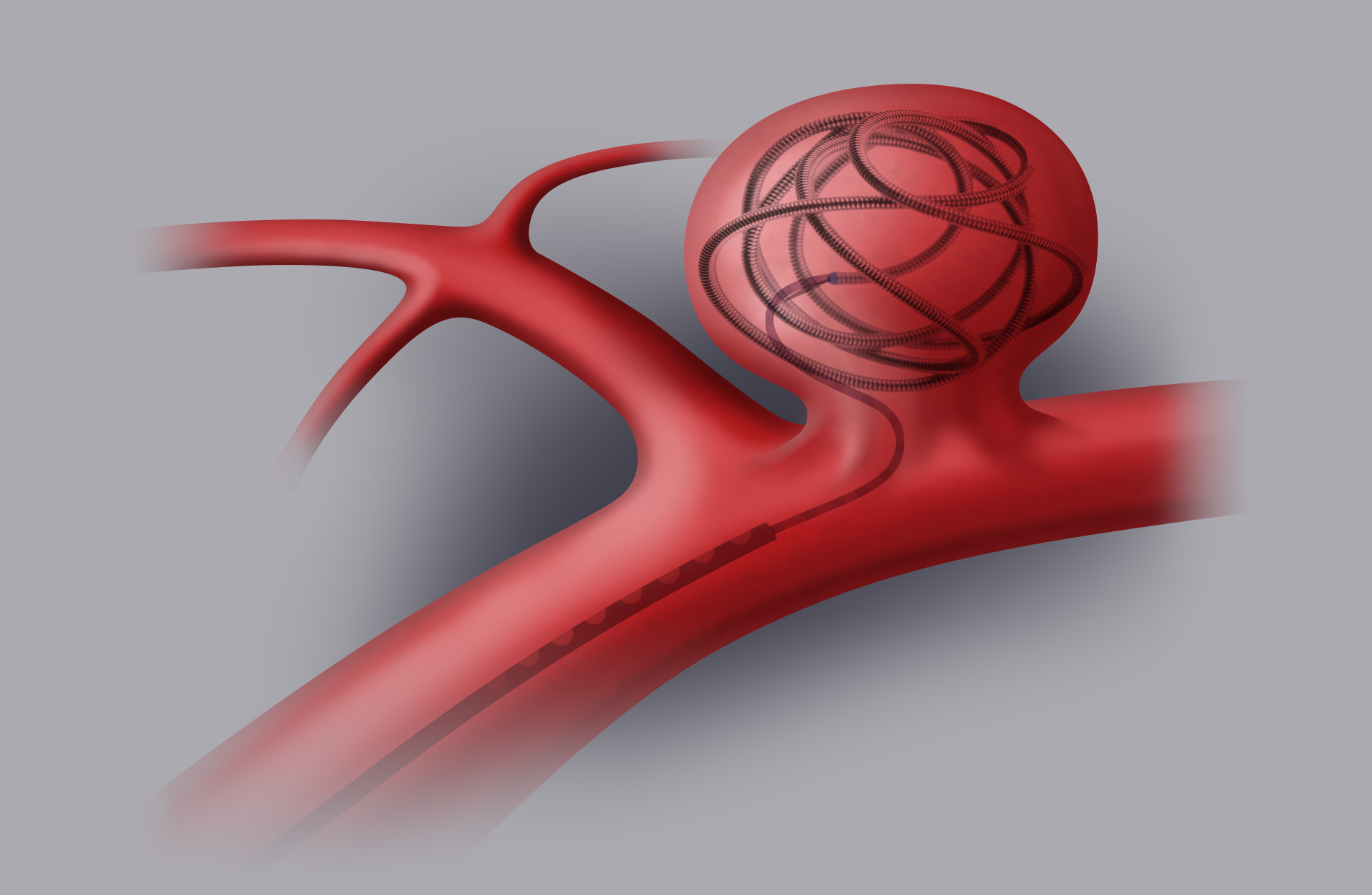
Endovascular treatment (coiling-stenting)
Endovascular treatment is a normal angiographic procedure. A microcatheter is introduced in the femoral artery in order to reach the inside of the sac thanks to radioscopic imaging. Then you proceed to fill the aneurysm by releasing platinum micro “spirals” (coils) inside the aneurysm itself. In other cases you may decide to place a stent on the stretch of the artery where the aneurysm sac has emerged.
The risks are related to the possibility of experiencing transitory or permanent ischemic attacks (higher risk with stents than with spirals) and to the possible rupture of the aneurysm during the procedure.
Despite the unquestionable advantage of being a mini-invasive procedure, the results of the endovascular treatment could however not be final and require periodical follow-up examinations in the years to follow.
Overall, it is impossible to determine which procedure is most effective. Every single case should be assessed both by the neurosurgeon and by the neuro-radiologist, since some aneurysms are more successfully treated surgically, and others, on the contrary, show the best results if they are treated with an endovascular methodology.
Familiarity
One of the most frequent questions patients ask if they have experienced or are experiencing a cerebral aneurysm is the following: will my children also have an aneurysm?
We have seen that in families where the parents are carriers of cerebral aneurysms, first-degree relatives (parents, children, siblings) have a likelihood of 9-11% to develop the same pathology. Other studies quantify this risk as being equal to 19-20%.
Without wanting to alarm anyone, it could be useful to prescribe first-degree relatives an intracranial Angio-MRI (a non-invasive examination that does not imply exposure to ionizing radiation or infusion of contrast medium) to exclude or identify the presence of an aneurysm.
Association with other diseases
Some systemic diseases can be associated with the development of intracranial aneurysms (polycystic kidney in adults, some connective tissue diseases, such as Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Marfan Syndrome).
Patients with a polycystic kidney are considered to be at a particularly high risk and for them an Angio-MRI screening is recommended.
Prevention
There is no true prevention program, since it is not possible to establish the natural history of an aneurysm with certainty, but we can only base ourselves on statistical calculations.
If an aneurysm is detected incidentally, a neurosurgeon must be consulted, and if there are no indications for treatment but only observation in time, it becomes imperative to periodically check the arterial blood pressure and above all to stop smoking.
In fact, it has been proven that cigarette smoke represents the biggest risk factor for the development and rupture of a cerebral aneurysm.